Java Recursion Eight Queen Problem Easy Example
We have discussed Knight's tour and Rat in a Maze problem in Set 1 and Set 2 respectively. Let us discuss N Queen as another example problem that can be solved using backtracking.
The N Queen is the problem of placing N chess queens on an N×N chessboard so that no two queens attack each other. For example, the following is a solution for the 4 Queen problem.
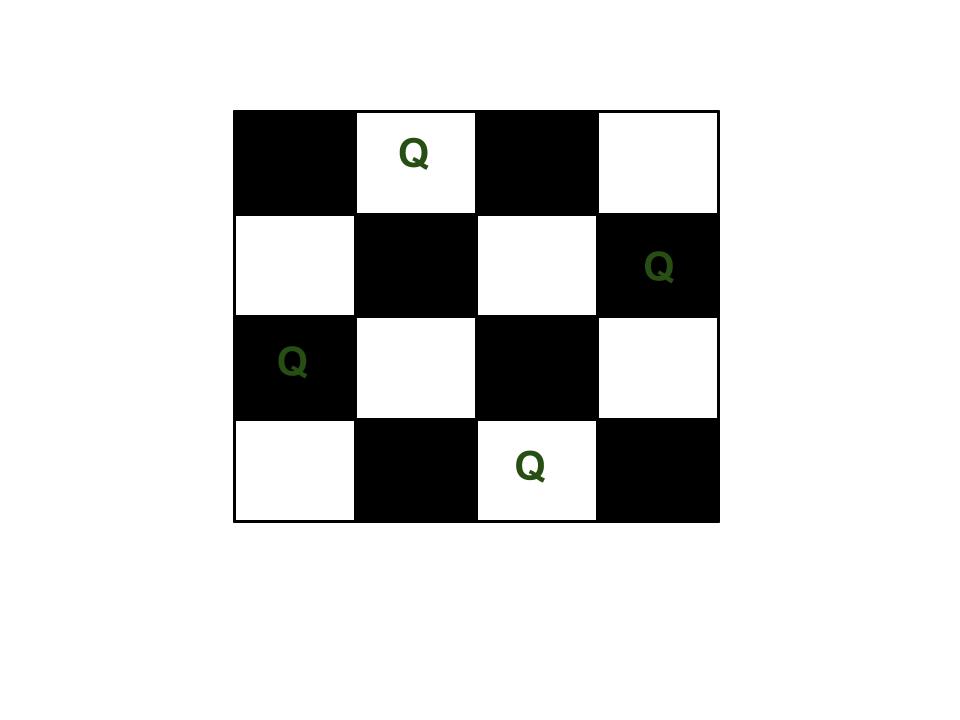 The expected output is a binary matrix that has 1s for the blocks where queens are placed. For example, the following is the output matrix for the above 4 queen solution.
The expected output is a binary matrix that has 1s for the blocks where queens are placed. For example, the following is the output matrix for the above 4 queen solution.
{ 0, 1, 0, 0}
{ 0, 0, 0, 1}
{ 1, 0, 0, 0}
{ 0, 0, 1, 0}
Naive Algorithm
Generate all possible configurations of queens on board and print a configuration that satisfies the given constraints.
while there are untried configurations { generate the next configuration if queens don't attack in this configuration then { print this configuration; } } Backtracking Algorithm
The idea is to place queens one by one in different columns, starting from the leftmost column. When we place a queen in a column, we check for clashes with already placed queens. In the current column, if we find a row for which there is no clash, we mark this row and column as part of the solution. If we do not find such a row due to clashes, then we backtrack and return false.
1) Start in the leftmost column 2) If all queens are placed return true 3) Try all rows in the current column. Do following for every tried row. a) If the queen can be placed safely in this row then mark this [row, column] as part of the solution and recursively check if placing queen here leads to a solution. b) If placing the queen in [row, column] leads to a solution then return true. c) If placing queen doesn't lead to a solution then unmark this [row, column] (Backtrack) and go to step (a) to try other rows. 4) If all rows have been tried and nothing worked, return false to trigger backtracking.
Implementation of Backtracking solution
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 4
using namespace std;
void printSolution( int board[N][N])
{
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for ( int j = 0; j < N; j++)
cout << " " << board[i][j] << " " ;
printf ( "\n" );
}
}
bool isSafe( int board[N][N], int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row][i])
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false ;
return true ;
}
bool solveNQUtil( int board[N][N], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true ;
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (isSafe(board, i, col)) {
board[i][col] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true ;
board[i][col] = 0;
}
}
return false ;
}
bool solveNQ()
{
int board[N][N] = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false ) {
cout << "Solution does not exist" ;
return false ;
}
printSolution(board);
return true ;
}
int main()
{
solveNQ();
return 0;
}
C
#define N 4
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void printSolution( int board[N][N])
{
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for ( int j = 0; j < N; j++)
printf ( " %d " , board[i][j]);
printf ( "\n" );
}
}
bool isSafe( int board[N][N], int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row][i])
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false ;
return true ;
}
bool solveNQUtil( int board[N][N], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true ;
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (isSafe(board, i, col)) {
board[i][col] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true ;
board[i][col] = 0;
}
}
return false ;
}
bool solveNQ()
{
int board[N][N] = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false ) {
printf ( "Solution does not exist" );
return false ;
}
printSolution(board);
return true ;
}
int main()
{
solveNQ();
return 0;
}
Java
public class NQueenProblem {
final int N = 4 ;
void printSolution( int board[][])
{
for ( int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) {
for ( int j = 0 ; j < N; j++)
System.out.print( " " + board[i][j]
+ " " );
System.out.println();
}
}
boolean isSafe( int board[][], int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0 ; i < col; i++)
if (board[row][i] == 1 )
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0 ; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j] == 1 )
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j] == 1 )
return false ;
return true ;
}
boolean solveNQUtil( int board[][], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) {
if (isSafe(board, i, col)) {
board[i][col] = 1 ;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1 ) == true )
return true ;
board[i][col] = 0 ;
}
}
return false ;
}
boolean solveNQ()
{
int board[][] = { { 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0 ) == false ) {
System.out.print( "Solution does not exist" );
return false ;
}
printSolution(board);
return true ;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
NQueenProblem Queen = new NQueenProblem();
Queen.solveNQ();
}
}
Python3
global N
N = 4
def printSolution(board):
for i in range (N):
for j in range (N):
print (board[i][j], end = " " )
print ()
def isSafe(board, row, col):
for i in range (col):
if board[row][i] = = 1 :
return False
for i, j in zip ( range (row, - 1 , - 1 ),
range (col, - 1 , - 1 )):
if board[i][j] = = 1 :
return False
for i, j in zip ( range (row, N, 1 ),
range (col, - 1 , - 1 )):
if board[i][j] = = 1 :
return False
return True
def solveNQUtil(board, col):
if col > = N:
return True
for i in range (N):
if isSafe(board, i, col):
board[i][col] = 1
if solveNQUtil(board, col + 1 ) = = True :
return True
board[i][col] = 0
return False
def solveNQ():
board = [ [ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ] ]
if solveNQUtil(board, 0 ) = = False :
print ( "Solution does not exist" )
return False
printSolution(board)
return True
solveNQ()
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
readonly int N = 4;
void printSolution( int [,]board)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for ( int j = 0; j < N; j++)
Console.Write( " " + board[i, j]
+ " " );
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
bool isSafe( int [,]board, int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row,i] == 1)
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 &&
j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i,j] == 1)
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 &&
i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i, j] == 1)
return false ;
return true ;
}
bool solveNQUtil( int [,]board, int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true ;
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (isSafe(board, i, col))
{
board[i, col] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1) == true )
return true ;
board[i, col] = 0;
}
}
return false ;
}
bool solveNQ()
{
int [,]board = {{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 }};
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false )
{
Console.Write( "Solution does not exist" );
return false ;
}
printSolution(board);
return true ;
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
GFG Queen = new GFG();
Queen.solveNQ();
}
}
Javascript
<script>
const N = 4
function printSolution(board)
{
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
document.write(board[i][j], " " )
}
document.write( "</br>" )
}
}
function isSafe(board, row, col)
{
for (let i = 0; i < col; i++){
if (board[row][i] == 1)
return false
}
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false
return true
}
function solveNQUtil(board, col){
if (col >= N)
return true
for (let i=0;i<N;i++){
if (isSafe(board, i, col)== true ){
board[i][col] = 1
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1) == true )
return true
board[i][col] = 0
}
}
return false
}
function solveNQ(){
let board = [ [0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0] ]
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false ){
document.write( "Solution does not exist" )
return false
}
printSolution(board)
return true
}
solveNQ()
</script>
Output
0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
Time Complexity: O(N!)
Auxiliary Space: O(N2)
Optimization in is_safe() function
The idea is not to check every element in right and left diagonal, instead use the property of diagonals:
1. The sum of i and j is constant and unique for each right diagonal, where i is the row of elements and j is the
column of elements.
2. The difference between i and j is constant and unique for each left diagonal, where i and j are row and column of element respectively.
Implementation of Backtracking solution(with optimization)
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
int ld[30] = { 0 };
int rd[30] = { 0 };
int cl[30] = { 0 };
void printSolution( int board[N][N])
{
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for ( int j = 0; j < N; j++)
cout<< " " << board[i][j]<< " " ;
cout<<endl;
}
}
bool solveNQUtil( int board[N][N], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true ;
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1] != 1 && rd[i + col] != 1) && cl[i] != 1) {
board[i][col] = 1;
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true ;
board[i][col] = 0;
ld[i - col + N - 1] = rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 0;
}
}
return false ;
}
bool solveNQ()
{
int board[N][N] = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false ) {
cout<< "Solution does not exist" ;
return false ;
}
printSolution(board);
return true ;
}
int main()
{
solveNQ();
return 0;
}
C
#define N 4
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
void printSolution( int board[N][N])
{
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for ( int j = 0; j < N; j++)
printf ( " %d " , board[i][j]);
printf ( "\n" );
}
}
bool isSafe( int board[N][N], int row, int col)
{
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < col; i++)
if (board[row][i])
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; i >= 0 && j >= 0; i--, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false ;
for (i = row, j = col; j >= 0 && i < N; i++, j--)
if (board[i][j])
return false ;
return true ;
}
bool solveNQUtil( int board[N][N], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true ;
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (isSafe(board, i, col)) {
board[i][col] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true ;
board[i][col] = 0;
}
}
return false ;
}
bool solveNQ()
{
int board[N][N] = { { 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false ) {
printf ( "Solution does not exist" );
return false ;
}
printSolution(board);
return true ;
}
int main()
{
solveNQ();
return 0;
}
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int N = 4 ;
static int []ld = new int [ 30 ];
static int []rd = new int [ 30 ];
static int []cl = new int [ 30 ];
static void printSolution( int board[][])
{
for ( int i = 0 ; i < N; i++)
{
for ( int j = 0 ; j < N; j++)
System.out.printf( " %d " , board[i][j]);
System.out.printf( "\n" );
}
}
static boolean solveNQUtil( int board[][], int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < N; i++)
{
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1 ] != 1 &&
rd[i + col] != 1 ) && cl[i] != 1 )
{
board[i][col] = 1 ;
ld[i - col + N - 1 ] =
rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 1 ;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1 ))
return true ;
board[i][col] = 0 ;
ld[i - col + N - 1 ] =
rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 0 ;
}
}
return false ;
}
static boolean solveNQ()
{
int board[][] = {{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 },
{ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 }};
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0 ) == false )
{
System.out.printf( "Solution does not exist" );
return false ;
}
printSolution(board);
return true ;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
solveNQ();
}
}
Python3
N = 4
ld = [ 0 ] * 30
rd = [ 0 ] * 30
cl = [ 0 ] * 30
def printSolution(board):
for i in range (N):
for j in range (N):
print (board[i][j], end = " " )
print ()
def solveNQUtil(board, col):
if (col > = N):
return True
for i in range (N):
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1 ] ! = 1 and
rd[i + col] ! = 1 ) and cl[i] ! = 1 ):
board[i][col] = 1
ld[i - col + N - 1 ] = rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 1
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1 )):
return True
board[i][col] = 0
ld[i - col + N - 1 ] = rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 0
return False
def solveNQ():
board = [[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ],
[ 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 ]]
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0 ) = = False ):
printf( "Solution does not exist" )
return False
printSolution(board)
return True
solveNQ()
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int N = 4;
static int []ld = new int [30];
static int []rd = new int [30];
static int []cl = new int [30];
static void printSolution( int [,]board)
{
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for ( int j = 0; j < N; j++)
Console.Write( " {0} " , board[i, j]);
Console.Write( "\n" );
}
}
static bool solveNQUtil( int [,]board, int col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true ;
for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1] != 1 &&
rd[i + col] != 1) && cl[i] != 1)
{
board[i, col] = 1;
ld[i - col + N - 1] =
rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true ;
board[i, col] = 0;
ld[i - col + N - 1] =
rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 0;
}
}
return false ;
}
static bool solveNQ()
{
int [,]board = {{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0 }};
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false )
{
Console.Write( "Solution does not exist" );
return false ;
}
printSolution(board);
return true ;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
solveNQ();
}
}
Javascript
<script>
let N = 4;
let ld = new Array(30);
let rd = new Array(30);
let cl = new Array(30);
function printSolution( board)
{
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (let j = 0; j < N; j++)
document.write(board[i][j] + " " );
document.write( "<br/>" );
}
}
function solveNQUtil(board, col)
{
if (col >= N)
return true ;
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if ((ld[i - col + N - 1] != 1 &&
rd[i + col] != 1) && cl[i] != 1)
{
board[i][col] = 1;
ld[i - col + N - 1] =
rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 1;
if (solveNQUtil(board, col + 1))
return true ;
board[i][col] = 0;
ld[i - col + N - 1] =
rd[i + col] = cl[i] = 0;
}
}
return false ;
}
function solveNQ()
{
let board = [[ 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0 ]];
if (solveNQUtil(board, 0) == false )
{
document.write( "Solution does not exist" );
return false ;
}
printSolution(board);
return true ;
}
solveNQ();
</script>
Output
0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
Time Complexity: O(N!)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Printing all solutions in N-Queen Problem
Sources:
http://see.stanford.edu/materials/icspacs106b/H19-RecBacktrackExamples.pdf
http://en.literateprograms.org/Eight_queens_puzzle_%28C%29
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eight_queens_puzzle
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/n-queen-problem-backtracking-3/
0 Response to "Java Recursion Eight Queen Problem Easy Example"
Post a Comment